Haulotte Rough Terrain Scissor Lifts Arlington
Industrial lifts have traditionally been utilized in production and manufacturing settings to help lift and lower supplies, workers, and goods. The scissor lift, also known as a table lift, is an industrial lift that has been modified for retail and wholesale environments.
Most customers who have been shopping in a store late at night have almost certainly seen a scissor lift, even if they do not know they have. Essentially, the scissor lift is a platform with wheels that performs like a lift truck. In a non-industrial environment, the scissor lift is great for completing tasks which need the speed or mobility and transporting of materials and people above ground level.
The scissor lift is unique, able to hoist workers straight up into the air. Instead, the scissor lift platform rises when the folding and linked supports underneath it draw together, making the equipment stretch upward. Once the equipment is extended, the scissor lift reaches around from 6.4 to 18.8 meters or 21 to 62 feet above ground. This depends on the size of the unit and the purpose.
The rough terrain scissor lifts could either be powered by an electric motor or by hydraulics, however, it could be a bumpy ride for the worker in the lift going to the top. The design of the scissor lift keeps it from traveling with a constant velocity, rather than traveling slower with more extension or traveling faster during the middle of its journey.
A really common class of scissor lift is the RT or Rough Terrain class. Typical features of the RT models comprise increased power due to the IC or internal combustion engine. The variations come in petrol, gas, combinations or diesel. This is needed to handle the increased weights and steeper grades of 18 to 22 degrees which are usually associated with this specific class of scissor lift.
- MEC Scissor Lifts Arlington
Safety Requirements for Scissor Lifts Scissor lift machinery are known as "moveable scaffolds," according to the OSHA. These industrial machines are capable of lifting heavy and large loads that are balanced well. They are responsible... More - Doosan Dual Fuel Forklifts Arlington
Basic Training Information for LPG Liquid petroleum gas or LPG is a odorless and colorless fuel derived from natural gas. LPG consists of 90% propane. It is extracted in a process referred to as distilling.... More - Mitsubishi Counterbalance Forklifts Arlington
Unfortunately, industrial accidents and injuries at construction sites are extremely common and occur more often than anybody would prefer. According to statistics, a huge majority of these mishaps occur because of inadequate or wholly absent... More - Taylor Reach Stackers Arlington
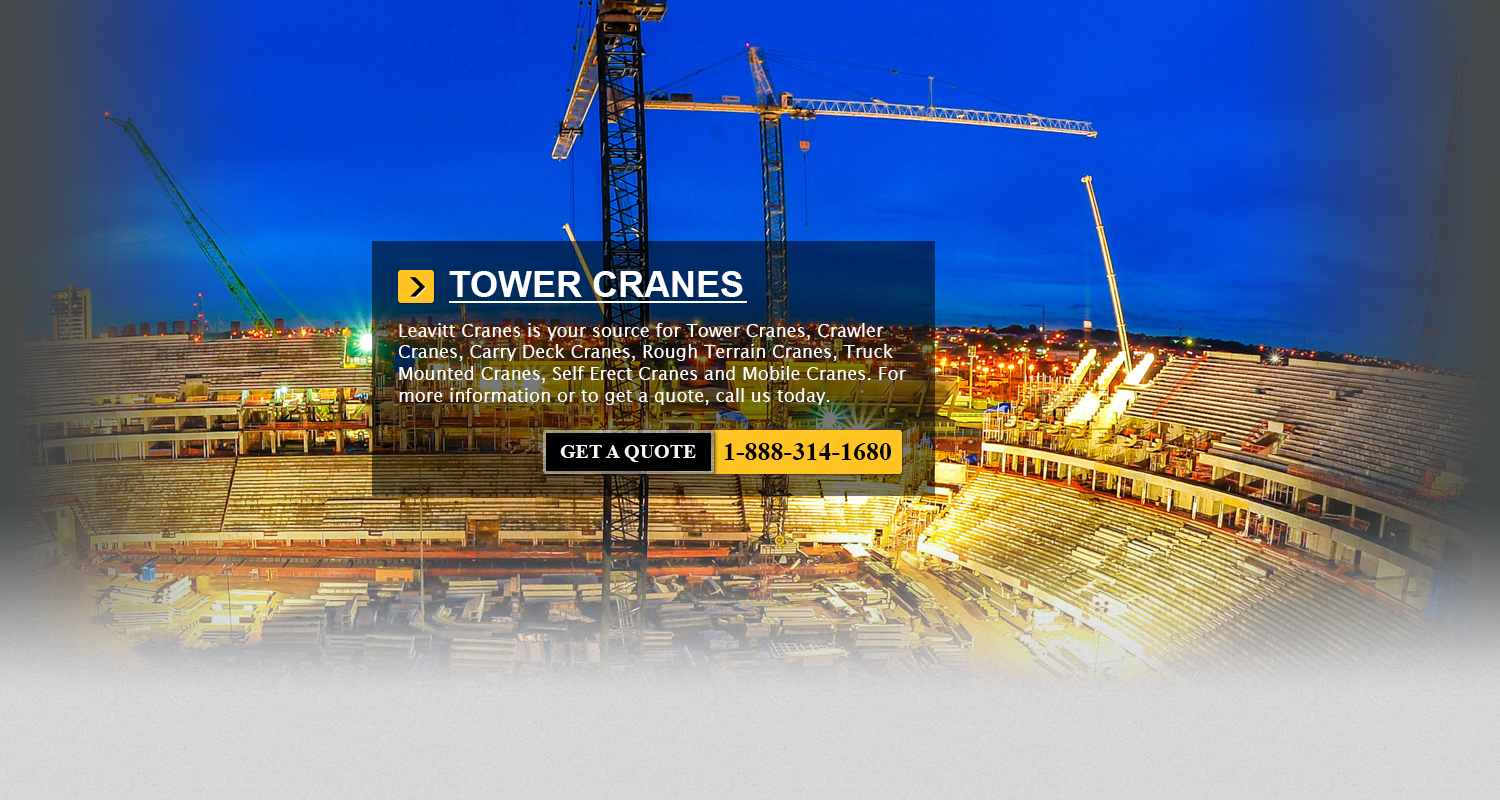
TS Series Reach Stackers Taylor has set a new standard with their newest reach stacker container handlers. Their newest TS-9972 Reach Stacker is a user friendly, really comfortable and durable machinery. The TS-9972 has all... More - Wolff Tower Cranes Arlington
During 1861, the company Harland and Wolff was formed. Mr. Gustav Wilhelm Wolff, born in Hamburg in 1834, along with Mr. Edward James Harland born during 1831, formed the business. In 1858 Harland, who was... More